Installing Splunk add-ons
Use this guide to install any Splunk-supported add-on to your Splunk platform. Also be sure to consult the specific installation instructions for an individual add-on if they are available.
Before you install an add-on
- Find the add-on that you want on Splunkbase.
- Read the documentation to verify that the add-on satisfies your use case and works for the version of software that you are using.
- Verify that your hardware and software meet the specific requirements specified in the documentation for the add-on.
- See the installation overview in the documentation for the add-on to familiarize yourself with the configuration steps necessary on the vendor software side and within your Splunk platform.
- See the installation instructions for the specific add-on to determine where you must install the add-on and to review additional requirements that might affect your installation.
Installation instructions
Download the add-on and install it on your Splunk platform, following the guide that matches your deployment scenario:
- Install an add-on in a single-instance Splunk Enterprise deployment
- Install an add-on in a distributed Splunk Enterprise deployment
- Install an add-on in Splunk Cloud Platform
- Install an add-on in Splunk Light (Legacy)
If you have questions about on what tiers of your Splunk platform architecture you must install a particular add-on and why, see Best practices on where to install Splunk add-ons and Advanced information for where to install add-ons. However, unless otherwise stated, you can safely install Splunk-supported add-ons to all tiers of your Splunk platform deployment without causing any problems.
Special considerations for using a deployment server to install an add-on
You can use the deployment server to install an add-on to your forwarders only if the add-on supports deployment servers for data collection nodes. Check the deployment instructions for each individual add-on to verify whether deployment servers are supported.
If the add-on uses modular or scripted inputs to collect data from remote sources, using a deployment server to deploy the configured add-on to multiple forwarders acting as data collectors causes duplication of data. This limitation applies to third-party deployment solutions as well as the deployment server.
You can safely use a deployment server to deploy unconfigured add-ons.
For more information about using a deployment server, see About deployment server and forwarder management in the Splunk Enterprise documentation.
Special considerations for using add-ons on search head clusters
Unless otherwise noted, add-ons are supported on search head clusters for search-time functionality, but not for data collection. To avoid creating duplicate inputs, do not configure inputs in a search head cluster.
Some add-ons require you to configure credentials and other settings on your search heads. For example, if the add-on includes workflow actions or search commands that require the search head to authenticate with the third-party technology, you must provide those credentials on your search heads. Configuring credentials on a search head cluster is supported for Splunk platform version 6.3 and later but not for previous versions.
If any step in your add-on configuration requires you to access a Setup page on a search head cluster node, click Settings > Show All Settings so that you can see the Setup link on your search head cluster node.
Summary of limitations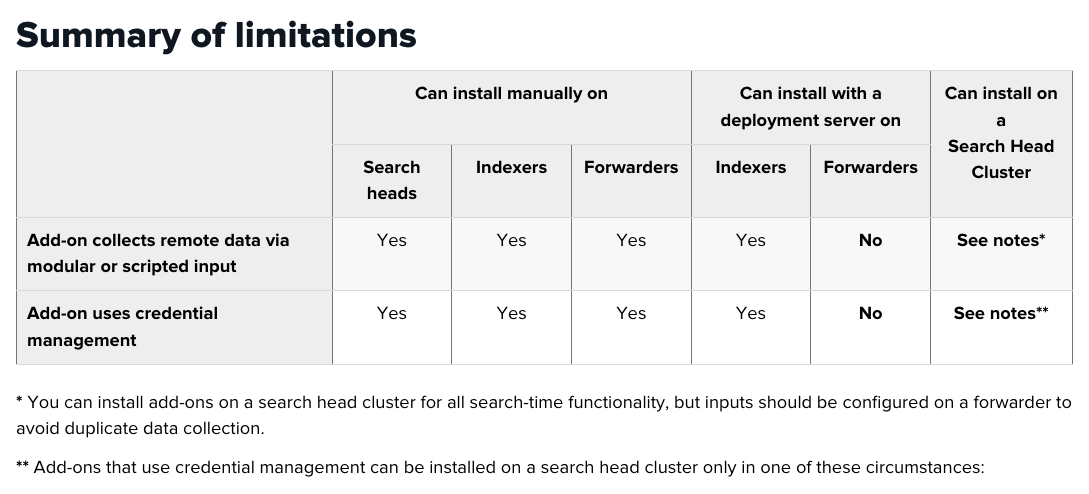
- You are using Splunk platform 6.3.X or later.
- You are using Splunk platform 6.2.X, and the credentials are not required on the search heads. If credentials are required only for data collection, set up a forwarder to handle the inputs and configure the credentials on that node. Some add-ons do require the search heads to communicate directly with a third-party system using stored credentials. These add-ons are not supported on search head clusters in 6.2.X.
Best practices on where to install Splunk add-ons
Unless otherwise noted, you can install any add-on to all tiers of your Splunk platform architecture – search tier, indexer tier, forwarder tier – without any negative impact. Splunk recommends installing Splunk-supported add-ons across your entire Splunk platform deployment, then enabling and configuring inputs only where they are required.
For example, if you install an add-on to your indexer tier, but the add-on does not have any index-time functionality, it does no harm to have it there. Add-on packages do not take up significant room on disk, so you can safely install them across your architecture.
Be sure to follow the specific configuration instructions for each individual add-on, and be aware of any limitations regarding using a deployment server.
Advanced information for where to install add-ons
If you prefer to install add-ons only to the locations they are required, consult the installation instructions for each individual add-on, which indicate where your add-on must be installed in order to work in a distributed architecture. Each add-on differs depending on what it contains, as shown in the diagram below.
- Add-ons that contain search-time functionality, such as dashboards, prebuilt panels, saved searches, macros, tags, data models, and lookups, need to be installed on your search heads.
- Add-ons that contain data manipulation functionality, usually in
props.confandtransforms.conffiles, should be installed on search heads, indexers, and forwarders, because that data manipulation could apply at various phases in the data pipeline: parsing, indexing, or search. Unless you are certain of where the data manipulation functions of the add-on occur, install it across all tiers of your architecture. - Add-ons that contain inputs belong on forwarders, and in some select cases also on search heads. Inputs that contain dynamic lookups need to be installed on search heads because they feed results back into the input directly from the search. Consult the documentation of the add-on for special instructions.
For more information about how Splunk software components correlate to phases in the data pipeline, see Configuration parameters and the data pipeline in the Splunk Enterprise documentation. The remaining sections in this chapter describe how to install an add-on in various deployment scenarios and to specific parts of your architecture.
